Looking for a Student Loan?
Learn more about student loans vs. financial aid below to learn more about the different ways you can contribute to the cost of your education.
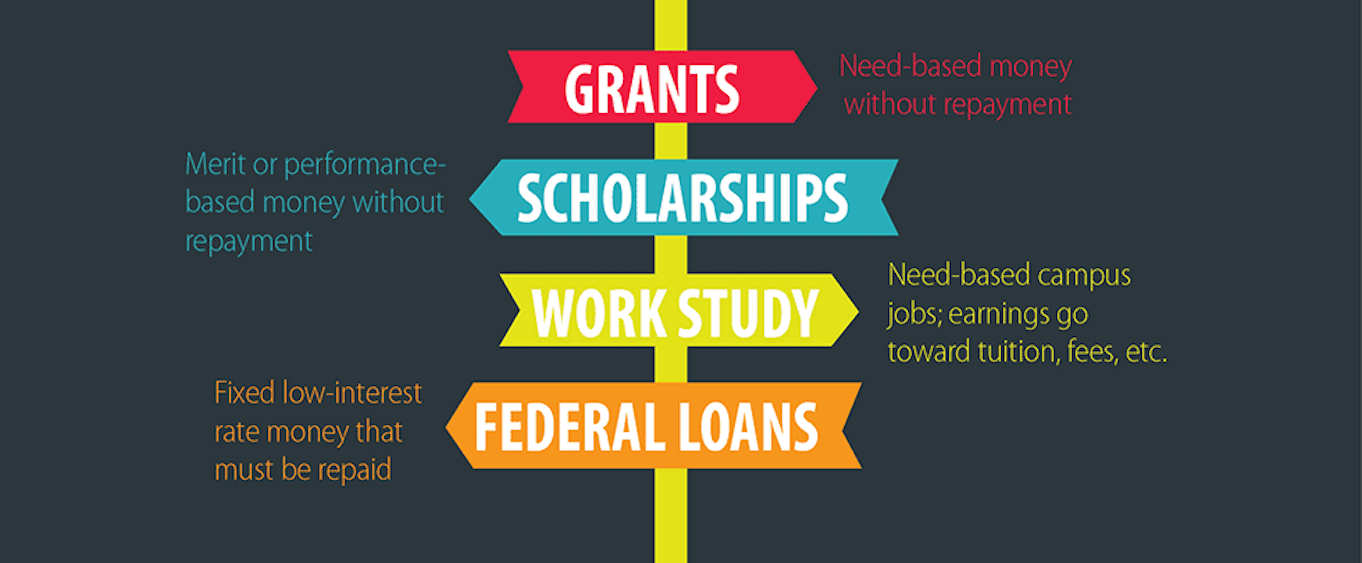
Student Loans vs. Financial Aid: What’s the Difference?
Financial aid and student loans may originate from the federal government or the private sector. The primary distinction between financial aid and student loans is whether or not the money you receive must be repaid. While financial assistance programs like grants and scholarships usually do not require repayment, student loans usually have an interest rate.
That distinction can make a big difference. “Every dollar you receive in scholarship or grant form is a dollar you don’t have to pay interest on,” says Zina Kumok, an editor at Dollar Sprout. And saving that money opens up possibilities after graduation, too. “Students who don’t have to take out as many loans will have more career options and afford to start their own businesses, work in lower-paying fields, or even take time off to travel abroad.”
However, before you sign anything, as with any financial arrangement, make sure you understand the terms. Not all financial aid comes without strings.
How to Apply for Financial Aid
You must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) in order to be eligible for federal loans and other forms of financial aid. If you are still a dependent, you may need to submit the FAFSA using some of your parents’ income information. Find the ideal personal loan match for you right now.

You must investigate the program in question and finish the necessary application procedures in order to apply for private loans and financial aid. For example, numerous colleges and universities frequently offer academic or extracurricular scholarships. To learn how to apply to these programs, you will need to visit the websites of those universities or get in touch with the financial aid offices at different institutions. Private scholarship programs will also follow their own procedures.
Credit is extended to you or your parents for the purpose of paying for college through student loans. It is necessary to repay student loans, but usually not until after you graduate from college. If you work in a public sector, for example, you may be eligible to apply for a student loan forgiveness program.
Subsidized and Unsubsidized FederalLoans
You might learn that you are eligible for federal loans when you submit an FAFSA application. Federal loans that are subsidized typically have slightly better terms than those that are not. One additional advantage of a subsidized loan is that, provided you fulfill enrollment requirements, the Department of Education will pay the interest on it. There are restrictions on the amount you can borrow, and interest rates start at 2. 75 to 4. 3%.
Read more about COVID-19’s financial safeguards and federal student loans in What You Need to Know about CARES, HEROES, and HEALS.
You can apply for private student loans from commercial lenders if you want an alternative or if you don’t qualify for federal student loans. Your credit score may determine whether you are approved for these loans or receive favorable terms and rates.
Join ExtraCredit to learn your credit score if you don’t already know it.
There are many different types of financial aid, and most of them don’t require repayment after you graduate. The government, other private organizations, or your school may provide these kinds of assistance. They are usually separated into two categories: merit-based aid and needs-based aid.
You must thoroughly study the requirements, deadlines, and payment details before submitting an application for any kind of financial assistance.
Be wary of scholarship and other aid programs that charge fees. “Fees are a dead giveaway of scholarship scams,” says Doug Whiteman, editor-in-chief at MoneyWise.com. “Be very careful about handing over a credit card number or other personal information.”
Scholarships are awarded for need or merit, and they’re offered by a wide range of organizations. Schools, private businesses, local and national associations, religious organizations, and charities are all potential sources for scholarships. Most scholarships do not require you to pay them back.
“Students should be more aggressive about applying for scholarships,” says Kumok. Whiteman agrees, citing a recent New York Times article that estimates there are 44,000 private scholarship programs. “The typical student probably has no idea that there’s so much money available,” he says. “Too often students and their families have seen student loans as an easy fallback, before they’ve fully explored scholarship and other financial aid possibilities.”
Grants are a type of financial aid that you typically don’t have to pay back. Federal and state governments offer grants, as do private and nonprofit organizations. Make sure to do ample research to ensure you get your application right, and pay attention to the grant terms. While many grants don’t have to be repaid, some do.
Be careful not to depend fully on grants, though. “Grants might not be available for the length of your degree program,” advises Anna Serio, a staff writer at Finder.com. “Some only cover the first year, while others are only available during the second, third, or fourth year of school. Even if a grant program covers all four years, you might have to reapply every year to be considered.”
Work-study positions assist you in covering costs or funding your education. Certain work-study positions are paid internships where you can put the knowledge and abilities you’re learning in class or for your future career into practice. Others might just be jobs that are available on campus in the writing centers, fitness centers, dining halls, or tutoring services.
The best options for students looking to strengthen their resumes are work-study programs, according to Serio “If you’re in graduate school, work-study can help you find a job in a new field or without experience.” Work-study positions can occasionally lead to regular part-time or full-time positions. ”.
If you pay qualifying expenses for school, you may be able to claim a certain amount as a tax credit to reduce your tax burden or even get a refund. The American Opportunity Credit, for example, allows up to $2,500 credit per eligible student, while the Lifetime Learning Credit allows qualified individuals to claim up to $2,000 for qualified education expenses per tax year.
Almost every state offers grants or other financial aid opportunities for college students. The National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators provides a detailed list of state financial aid opportunities.
Although schools may provide a lot of their own programs, they aren’t always widely disseminated Make it a point to visit the financial aid office whenever you are considering colleges, during the application process, or even after you have been accepted. Financial aid officers at the school can assist in making sure you’ve applied for all available financial aid.
If you already have a job, your employer may provide educational funding. Certain employers offer programs that reimburse all or a portion of the cost of degree programs in exchange for a set length of time spent working for them. Others cover the cost of one-time classes, workshops, and training seminars that will probably increase your value as an employee. Find out if your employer provides these benefits by speaking with your supervisor or the human resources division.
Leave no stone unturned when seeking financial aid for college. There are several initiatives to assist in paying for education for those in particular circumstances.
For example, the Educational and Training Vouchers Program provides assistance to those who are or were in foster care. The National Health Service Corps Loan Repayment Program helps pay for student loans for those who work at Indian Health Services facilities. Be creative! The Tall Clubs International Foundation has a scholarship program for college women who are 5’10” tall and men who are at least 6’2”. Consider what makes you unique and look for scholarship opportunities that may reward you for it.
Did you know that there are also some tuition-free schools around the United States? Residents of certain states may qualify for free tuition programs. Be sure to do your research into these schools, as you would with any other. “The programs in the US often require you to work in exchange for your degree,” says Serio. “This can help you develop valuable skills and gives you a leg up entering the job market after you graduate.”
Get the Financial Aid You Need
You have many options for financial aid if you need assistance paying for your education. For guidance and support, get in touch with the financial aid office at your university. Check out our resource center for additional details if you’d like to know more about your options for student loans.
Looking for a Student Loan?


FAQ
Is financial aid the same as a loan?
Financial aid can be obtained through federal work-study programs or as gift aid, which is money that is given without expectation of repayment. Student loans must be repaid within a given loan term. In addition to the requirement that students repay their student loans, interest is usually charged during the loan’s term.
Is financial aid a loan or free money?
The FAFSA will provide the opportunity for free money. It’s the tool that educational institutions use to determine your eligibility for financial aid. However, grants—which are essentially “free money”—OR loans or work study—which are not—since you have to work for them or repay them—may be available as forms of financial assistance.
Do I have to pay back financial aid?
The most common type of repayable financial aid is student loans, which typically come with interest added to the original loan amount. Federal student loans may be subsidized or unsubsidized. When you are enrolled in school and during any grace periods, the federal government bears the interest on your loan if it is subsidized.
Is FAFSA a loan or a grant?
The FAFSA is not a loan. It is an application form. Nonetheless, you can apply for federal student loans and financial assistance using the FAFSA. To apply for various forms of financial aid, such as grants, student employment, and federal student loans, use the FAFSA, or Free Application for Federal Student Aid.
Read More :
https://studentaid.gov/sites/default/files/federal-loan-programs.pdf
